Example Configuration
Example Jupyter Notebook autograding configurations can be found on the Submitty GitHub.
Required Fields
For autograding Jupyter Notebooks, the following fields must be included in your autograding configuration.
{
"autograding" : {
"submission_to_runner" : [ ... ],
"work_to_details" : [ ... ]
},
"autograding_method": "docker",
"container_options": {
"container_image": "..."
},
"allow_system_calls": [
...
]
}
The method for allowing certain system calls can be found in System Call Filtering. You may also need to pass in resource limit values or a max submission size.
"resource_limits" : {
"RLIMIT_NPROC" : 32,
"RLIMIT_FSIZE": 20971520 // 20 MB
},
"max_submission_size": 10485760, // 10 MB
RLIMIT_NPROC will allow the necessary resources for the script to execute a submitted Jupyter Notebook.
RLIMIT_FSIZE allows the script to save the notebook in Submitty. In this case, it allows at most a 20 MB file to be executed and saved.
Precommands
Because of the saved outputs, you will need to apply precommands to each testcase that requires files generated from the validation method.
{
"pre_commands" : [
{
"command" : "cp",
// Assuming the first testcase is the case where the validation method was run
"testcase" : "test01",
"source" : "{filename}*.*",
"destination" : "./"
}
],
...
},
Validation Method
We offer a validation method that parses the cells in Jupyter Notebooks for autograding. The script requires a single specified input notebook (the student’s submission) and outputs an executed version of the notebook. If the student has no restrictions on the naming convention for their submitted notebook, you can use a wildcard to expect any input.
"command": "jupyter_notebook_grader -i *.ipynb -o executed.ipynb"
The possible saved files based on parsed output are highlighted below.
| Cell Type | File Pattern | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Markdown | {filename}.txt | Contains raw markdown source from cell |
| Code | {filename}_source.txt | Contains Python source code from cell |
| {filename}_err.txt | Contains traceback if error occurs, otherwise empty | |
| {filename}_stdout.txt | Captures standard output (e.g., print() statements) | |
| {filename}_stderr.txt | Captures standard error streams | |
| {filename}_result.txt | Text representation of cell’s result | |
| {filename}.png | Generated image outputs |
By default, the filenames are generated based on the index of the cell in the notebook, starting from 1.
Submitty IDs
Instructors can add Submitty IDs to mark specific cells in Jupyter Notebooks to grade. These specified IDs will replace the default filename of the saved output (e.g. cell1.txt –> {submitty_id}.txt). If students modify their provided Jupyter Notebook to be out of order, this method will correctly find the cell to grade. Note that your autograding configuration will also need to match the name of the saved file.
{
"pre_commands" : [
{
"command" : "cp",
"testcase" : "test01",
"source" : "{submitty_id}*.*",
"destination" : "./"
}
],
"title": "STDOUT",
"points": 1,
"validation": [
{
"method": "diff",
"actual_file": "{submitty_id}_stdout.txt",
"expected_string" : "hello world!"
}
]
}
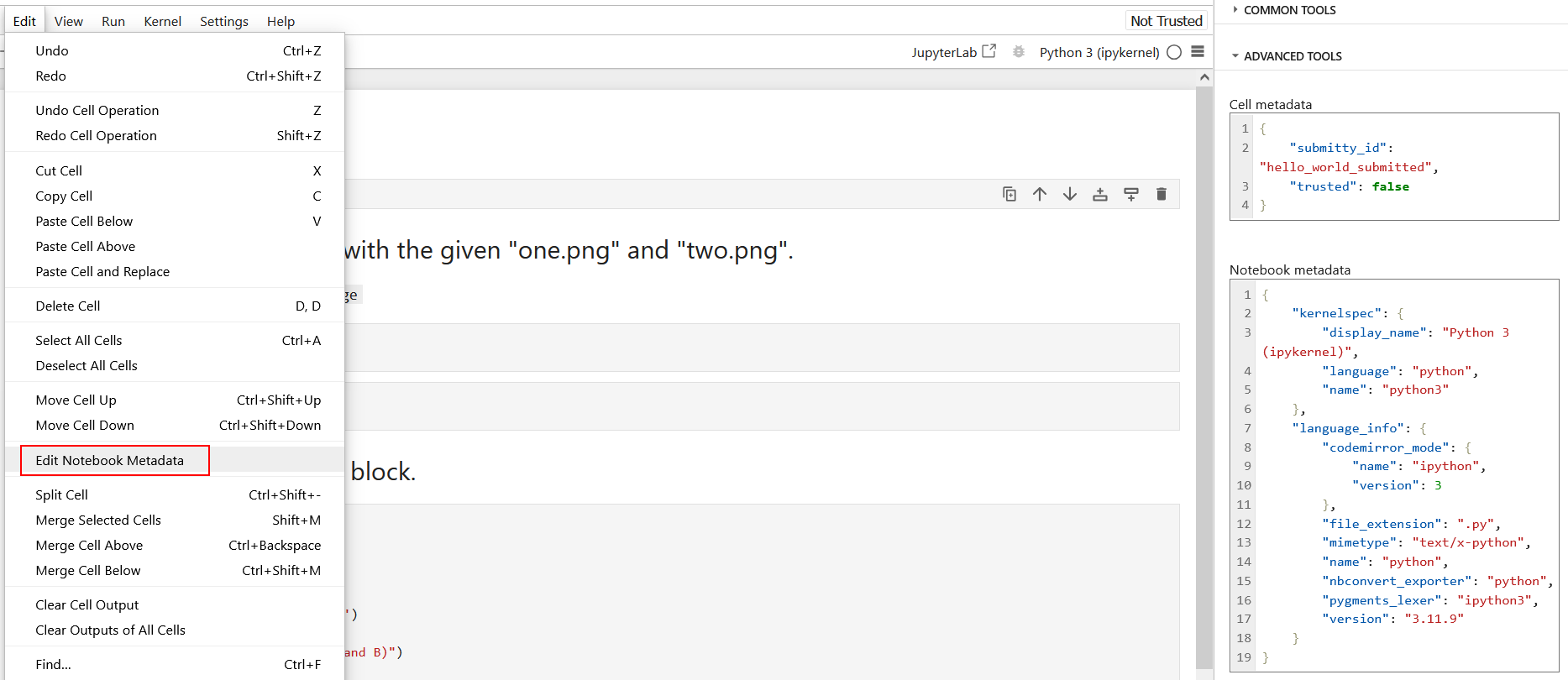
Jupyter Notebook provides an option to easily edit cell metadata, introduced in 7.1.0. In the Edit dropdown, you can find
Edit Notebook Metadata. An editor panel will open on the right side of your screen to easily type in the metadata.
An alternative option would be to manually edit the Jupyter Notebook JSON itself to include the submitty_id property in a cell’s metadata.